<< Hide Menu
8.9 Treatment of Disorders from the Biological Perspective
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Haseung Jun
A major perspective not covered in the previous section is biological psychology, which is where medication is utilized. Mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and many other types of disorders may be caused by a mixture of previously listed factors and a chemical imbalance.
The study of drugs 💊 on the mind and on our behavior, or psychopharmacology, is one of the ways biological psychologists treat disorders. Antidepressants, mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antianxiety drugs are all examples of biological solutions to psychological problems.
When a drug is first made, researchers have to test how effective it is using an experiment 🧪 The experimental group would receive the new drug and the control group would receive the placebo. Random assignment, random selection, and a double-blind procedure must be used.
Types of Drugs
Antidepressants
As said by the name, antidepressants are used to treat depression, anxiety, OCD, and PTSD. Most antidepressants are SSRIs, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SNRIs, which are selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
These drugs increase one's serotonin and norepinephrine levels, promoting neurogenesis 🌱 It takes a while to see the effect of these drugs because of neurogenesis, but the best way to treat depression is drugs, therapy, and exercise 🏃, combined.
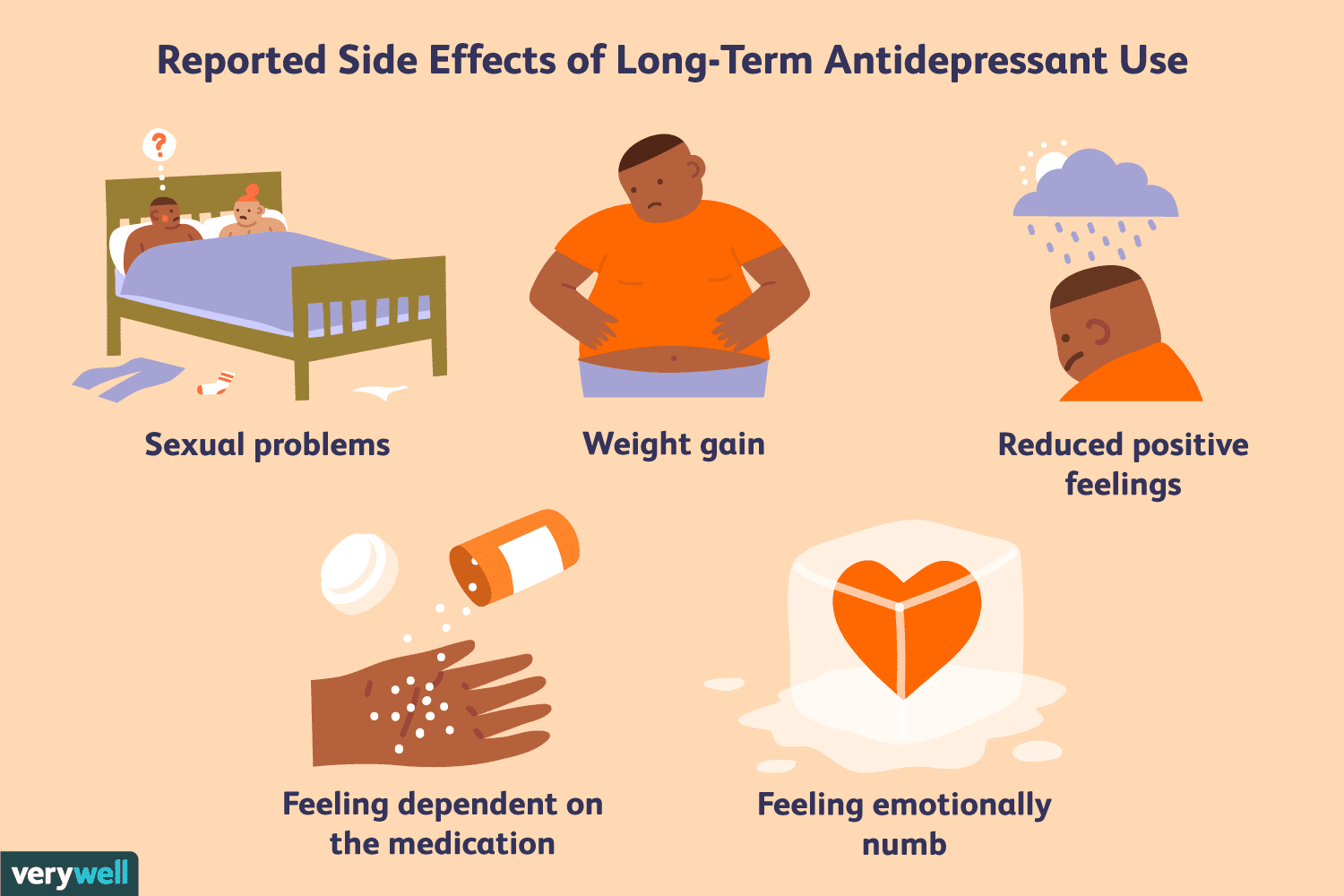
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Anti-anxiety Drugs (Tranquilizers)
As said by the name again, anti-anxiety drugs are used to treat anxiety disorders. Since anxiety occurs as a result of activity in the central nervous system, anti-anxiety drugs reduce CNS activity.
However, anti-anxiety drugs can become addicting, which creates further issues once the anxiety subsides. This can lead to the build up tolerance to these drugs and can lead to addiction, creating withdrawal symptoms when you stop using them.
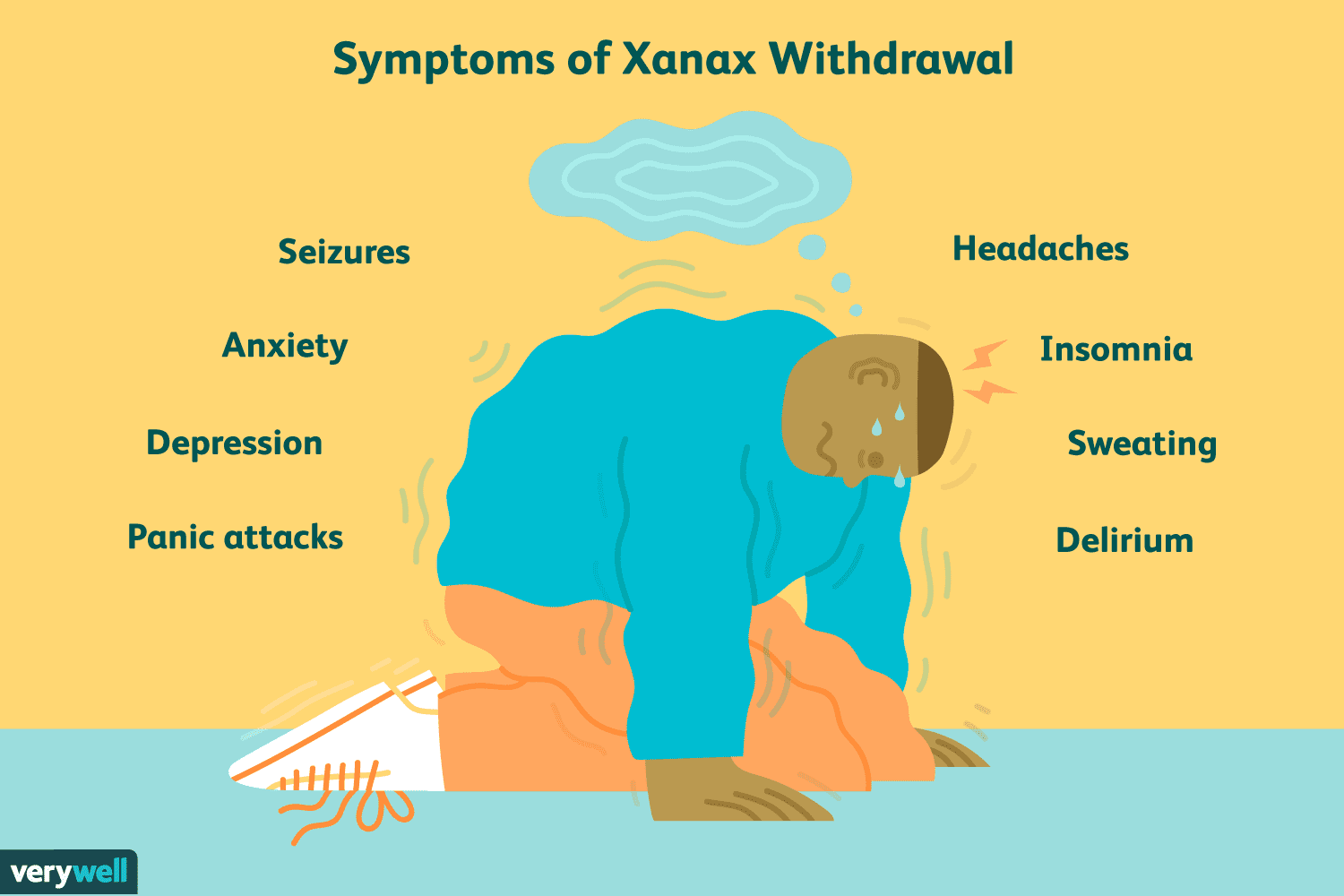
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Mood Stabilizers
Mood stabilizers help those with bipolar disorder. They balance both sides of the disorder: mania and depression.
Antipsychotic Drugs
Often called neuroleptics, these drugs help treat people with disorders like schizophrenia by decreasing dopamine levels. However, there is a huge negative effect to taking these drugs. Long-term use of antipsychotic drugs can cause tardive dyskinesia. You could think of this as tremors or twitches; it is basically the involuntary movements of your muscles. This results from the blocking of dopamine at other sites. Because of these side effects, many patients abandon the use of these medications, which can result in the return of any psychotic symptoms, brining you back to square one.

Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Table Summary
| Drug Type | Treats/How it works | Example/Disadvantages |
| Antidepressants—SSRI/SNRI | Depression and anxiety Increases serotonin or norepinephrine levels | Prozac, Zoloft, CelexaCan take weeks to notice changes in mood |
| Anti-anxiety—Benzodiazepines | Anxiety-Panic Attacks Depresses central nervous system | Xanax, Klonopin Build a tolerance, physical dependence |
| Mood Stabilizers | Bipolar disorder | Lithium |
| Antipsychotics | Schizophrenia Decreases dopamine levels | Abilify, Seroquel |
Other Procedures
Other than drugs, therapies and other biomedical procedures exist. Here are some you should be familiar with:
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
This is a type of therapy used with those that are severely depressed. The client would be given an anesthetic and then brief electric currents would be sent to their brain.
Because of the anesthesia, clients don't remember the whole procedure and after a few sessions of this, 80% of the depression fades away.
Well . . . why does this work? It is said that the shocks do what the medicine does: it lowers the activity of the brain and promotes neurogenesis (the formation of new neurons).
This is still used today, but very rarely, and in briefer currents. However, there is a chance of relapse after ECT.
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
rTMS is usually used for those with ASD (autism spectrum disorder) or depression. It is similar to ECT, but instead of electric currents, magnetic energy is sent to the brain.
These magnetic currents 🧲 either stimulate or suppress activity in the brain, and it is very painless and quick.
Many think it works because the magnetic energy might be activating the brain's left frontal lobe, which is associated with positive emotions and usually shrinks when people have depression.
Deep-brain Stimulation
Deep-brain stimulation isn't the most effective, but it helps with depression and possibly OCD.
Helen Mayberg found an area in the brain that helped activate the frontal lobes and the limbic system. She created a procedure in which she would connect this area of the brain to other areas of the brain to try and treat depression.
Psychosurgery👨⚕️
Psychosurgery is when a part of the brain is removed to ease or treat a disorder. This is very dangerous and basically never used because of how it could affect the brain. Back in the day, from 1935 to 1955, the prefontal lobotomy, which is the removal of the frontal lobes, was popular among patients. Unfortunately, this was done without much information and left patients as emotional zombies.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.