<< Hide Menu
8.8 Psychological Perspectives and Treatment of Disorders
6 min read•june 18, 2024
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Jillian Holbrook
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Jillian Holbrook
As covered briefly in previous units, psychology can be approached from a variety of perspectives. Each perspective has unique methodologies to treat psychological disorders by focusing on different target areas.
The three general therapeutic approaches are:
- 💊 Biomedical Therapy—drugs can be used to relieve physical or physiological pain
- 🛋️ Eclectic Approach—uses techniques from different types of therapies
- 🗣️ Talk Therapy—a collection of approaches that involve talking to the client or group/family therapy
Different Perspectives
Behavioral Psychology
The basis of behavioral psychology is identifying learned behaviors and using conditioning and or reinforcement for corrections. The past may be referenced in attempts to discover when the harmful behaviors were learned.
Behavior therapy uses counterconditioning, which is essentially using classical conditioning to create new conditioned responses. Through counterconditioning, undesirable reactions and behaviors can be replaced.
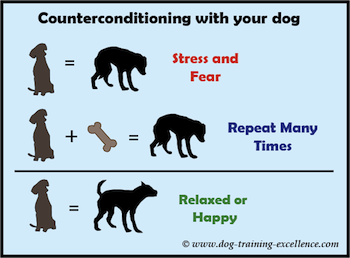
Image Courtesy of Dog Training Excellence.
Systematic Desensitization
Using the idea of counterconditioning, Mary Jones introduced exposure therapy and, specifically, systematic desensitization. Systematic desensitization includes pairing a stimulus of fear with relaxation techniques and conditioning the subject to associate the stimulus with relaxation rather than fear.
Systematic desensitization uses hierarchies. Take an example where a patient has a phobia of bees. First, the therapist would engage the patient to determine why the patient finds bees frightening. Next, they would ask the client to relax and gradually work them through visualizing bees or examining pictures of them. Through repetition, the patient will experience greater relaxation when presented with a bee-related visual stimulus. 🐝
Once that happens, the client may be asked to imagine an anxiety-arousing scene with bees involved. The patient will return to the relaxation technique if moving up the hierarchy induces anxiety. Slowly over time, the aim of this approach is to help the patient acclimate to their phobia and learn coping skills to overcome it.

Systemic desensitization hierarchy for arachnophobia. Image Courtesy of Psychology4A.
Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
When an anxiety is too difficult to recreate with systematic desensitization, therapists may use virtual reality exposure therapy to help their patients interact with stimuli.
Aversive Conditioning
Aversive conditioning includes conditioning something unpleasant with one's addiction. For example, substance use disorders are very difficult to beat. If one uses aversive conditioning to condition nausea with alcohol, the client will, eventually, no longer be inclined to drink alcohol due to associating it with feeling sick. 🤢
Behavior Modification
Using behavior modification, therapists encourage wanted behaviors with reinforcement and discourage negative behaviors. Some use a token economy, where clients earn a "token" for doing a desired behavior, and as the tokens accumulate, the client can exchange them for a reward.💰 Whether or not this is ethical is debated, but behavior modification does not usually help with extreme psychological disorders.
Cognitive Psychology
Unlike behavioral psychology, cognitive psychology places emphasis on current thoughts, behaviors, and other parts of cognition. Cognitive therapists believe that thinking "colors" our feelings, so we must think differently to develop positive, normalized feelings. 🙃
Therapy may consist of working through problems in both real and hypothetical situations to develop problem-solving skills. An example of cognitive therapy is Rational-Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), which challenges people to think otherwise and enables healthier behaviors. Think of REBT as reversing irrational beliefs.
Image Courtesy of Psychodynamic Techniques.
Humanistic Psychology
Humanistic psychology provides more individualism in treatment planning than other approaches. This non-deterministic approach popularized by Carl Rogers states that humans are innately good and capable of change. Client-centered talk therapy is the primary treatment method.
Carl Rogers tries to grow the self-awareness of his patients, which in turn, grows self-acceptance. 🌠 Rather than focusing on one's disorder and curing it, he focuses on helping them reach self-actualization. Unlike Freud and his psychodynamic theory, Rogers focuses on the present and the future.
Client-centered talk therapy focuses on promoting active listening in an accepting, genuine, and empathic environment. Don't forget unconditional positive regard! Active listening is where Rogers would simply listen, repeat, restate, and clarify what the patient said. This makes it so they don't change the client's thoughts or perspectives on anything.
Remember: Rogers paraphrased, confirmed, and allowed for reflection on the client's thoughts. The more they spoke about and clarified their feelings, the more the disorder slowly disappeared.
Psychodynamic Psychology
According to psychodynamic psychology, behavior is influenced by unconscious motives through the id, superego, and ego. Freud believed that these unconscious, uncontrollable urges and motivations lead to disorders and irrational thinking. A person’s childhood may be analyzed to determine the root of current problems. This approach is one of the most important ones to know for the AP exam.
He focused on four main things:
- Bringing unconscious thoughts into awareness, providing an insight into where the disorder may be coming from. This gets rid of the disorder from the inside. 💭
- Using free association, Freud would look for mental blocks (stopping mid-thought to prevent saying something or changing the subject), which show resistance. ⚠️
- Freud would see these mental blocks and how people tried to defend themselves, and he began to interpret why these blocks existed.
- Eventually, the patient would become more open and comfortable, expressing feelings with no problem (whether they be negative or positive). When the patient did this, Freud would think they are transferring thoughts experienced in the past into the present. This then provides insight to complete the cycle.
Insight → Resistance? → Interpretation → Transference
Psychodynamic Theories
Psychodynamic psychologists focus on fast therapy and providing immediate relief through understanding feelings and learning about yourself. Rather than thinking about the past, they focus on current relationships.
Cognitive-Behavioral Psychology
The cognitive-behavioral approach uses concepts and theories from both the cognitive and behavioral approaches. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is the primary type of therapy used in this approach due to its combination of perspectives.
CBT
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is one of the most widely practiced therapies and most successful. It aims to change the way someone thinks and acts (hence its name).
Those who undergo CBT learn that their negative thoughts are irrational and begin to replace them with a positive way of thinking. CBT works with anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and anorexia.

Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Rather than thinking negatively and extending their depression, people with mood disorders begin to replace their thinking and redirect their energy in ways that reward them and make them feel good.
Sociocultural Psychology
Sociocultural psychology contextualizes personal development within societal expectations and norms. The psychology of an individual is heavily shaped by those factors, as well as interactions between other people and cultures.
Effectiveness of Approaches by Disorder
| Approach | Best When Treating . . . |
| Behavioral | any disorders that lead to abnormalities in behavioral patterns or patients with a history of trauma |
| Cognitive | disorders where cognition behind thoughts and behaviors is affected or people who cannot rationally problem solve |
| Humanistic | interpersonal problems, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, or personality disorders |
| Psychodynamic | people with a history of unresolved trauma |
| Sociocultural | a broad range of disorders throughout a variety of different cultures |
Factors of Treatment
Treatment success is not only affected by the disorder and type of treatment, but also by many other variables. Cultural stigma of mental illness, socioeconomic status, life outlook, environment, and demographic information are all capable of impacting this!

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.