<< Hide Menu
8.3 Neurodevelopmental and Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Jillian Holbrook
Emily Pedrazzi
Dalia Savy
Jillian Holbrook
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Neurodevelopmental disorders are caused by unusual brain development, brain damage, or any other abnormality in the brain. The most commonly addressed neurodevelopmental disorders on the exam are Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and intellectual disabilities.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
ASD is characterized by atypical behaviors, speech, interests, thought patterns, and interpersonal interactions. People with ASD have a difficult time interpreting social cues and may prefer routine over spontaneity.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
ADHD is marked by the appearance of one or more symptoms:
- Extreme inattention
- Hyperactivity
- Impulsivity
ADHD is inheritable and can be treated with medications that calm the above symptoms. It often exists with another disorder, specifically a learning disorder or emotional disorder.
Those who are skeptics of ADHD simply blame impulsiveness on the presence of the Y chromosome. They believe that in a boring environment, the child will be energized and improperly diagnosed with ADHD. There is generally a lot of disagreement about ADHD and if it really is a neurodevelopmental disorder .🤷
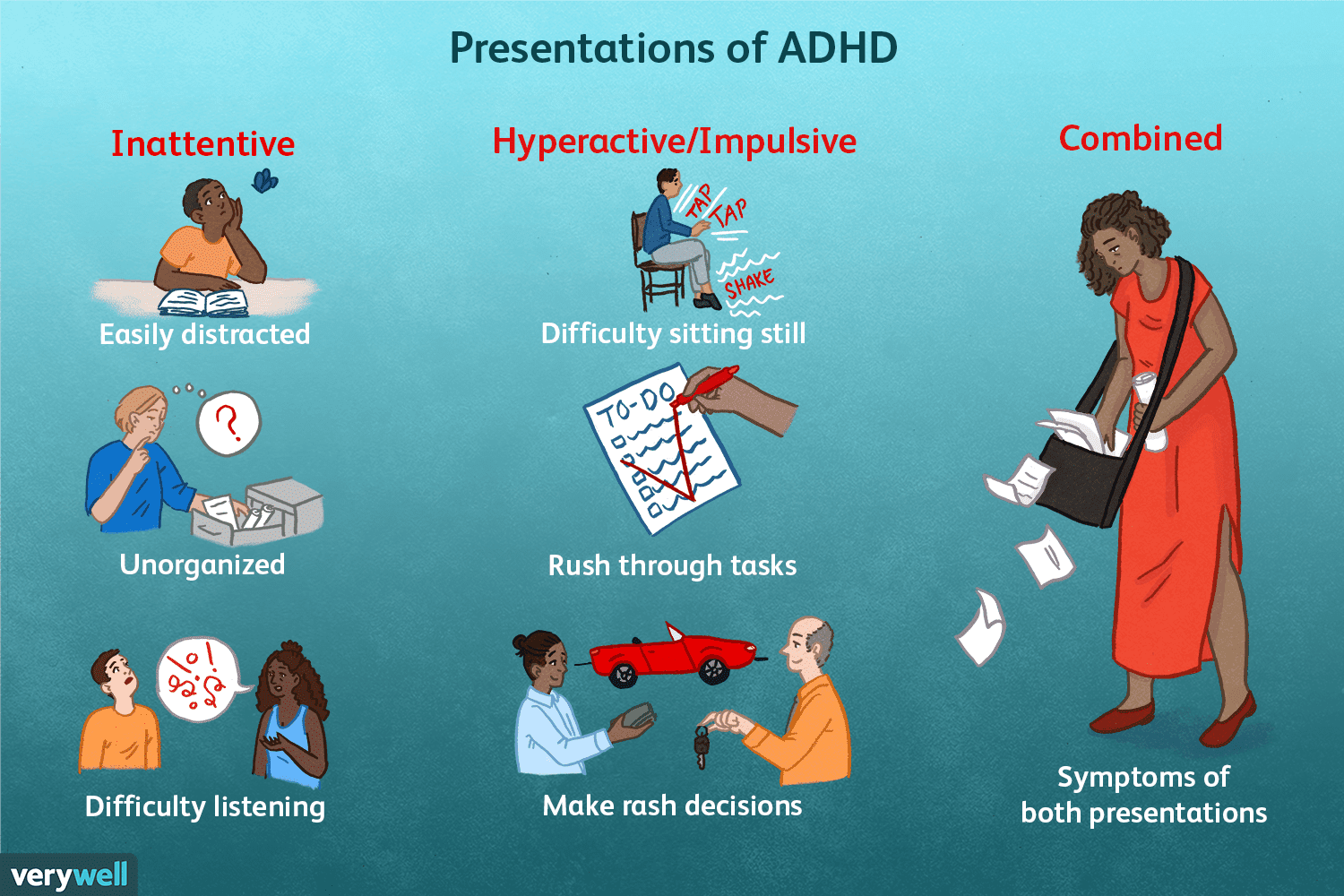
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Intellectual Disability
Having an IQ below 70 often means that there is some sort of intellectual disability that causes a person to:
- have limitations in learning
- have a hard time solving problems
- have difficulty communicating
- lack in many skills needed for everyday life
People with intellectual disabilities have trouble adapting to the demands of life that require conceptual, social, and practical skills. An example of an intellectual disability is Down Syndrome, also known as trisomy 21.
Neurocognitive Disorder
A neurocognitive disorder is a decrease in mental functioning caused by a somatogenic cause. Examples include breathing conditions, brain trauma, and cardiovascular disorders.
The most common neurocognitive disorder is Alzheimer's disease, which is a type of dementia that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is a progressive disease, which means that it gets worse over time. In the early stages of Alzheimer's, a person may have trouble remembering recent events or conversations and may have difficulty performing familiar tasks. As the disease progresses, a person with Alzheimer's may struggle with speaking, understanding, and communicating, as well as requiring help with daily activities such as bathing and dressing. Eventually, a person with Alzheimer's can lose the ability to recognize friends and family and may become completely dependent on others for their care.
Common symptoms include:
- 🧠 Short-term memory loss
- 🤕 Headaches
- 🚗 Difficulty walking and driving
- 😩 Inability to focus
There is no cure for Alzheimer's disease, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for people with the disease.
Psychotic and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder that impacts an individual’s perception of reality. During a psychotic episode, people may experience improbable or possible delusions and auditory and/or visual hallucinations.
Schizophrenia is an example of psychosis in which a person loses complete contact with reality and experiences false sensations.
Subtypes of Schizophrenia
There are many types of schizophrenia, and their symptoms greatly vary.
Acute Schizophrenia
Acute Schizophrenia is developed rapidly after a period of stress. People with this variant have more positive symptoms and are responsive to therapy, so recovery is possible. Positive symptoms are added symptoms, such as delusions and hallucinations. They add to a person's personality.
- Delusions, or false beliefs, can be erotomanic, grandiose, jealous, persecutory, somatic, or mixed.
- Hallucinations, or false sensory experiences, are often auditory👂
Chronic Schizophrenia
Chronic Schizophrenia is slow and develops over time. Those with chronic schizophrenia exhibit negative symptoms. Recovery is doubtful. Negative symptoms remove from a person's personality. Some examples include:
- Inability to feel emotion
- Difficulty understanding emotion
- Difficulty reading others' emotions
- Flat speech
- Impaired attention
- Lack of pleasure
- Catatonia— Being motionless for hours and agitated shortly after
- Flat Affect—emotionless state
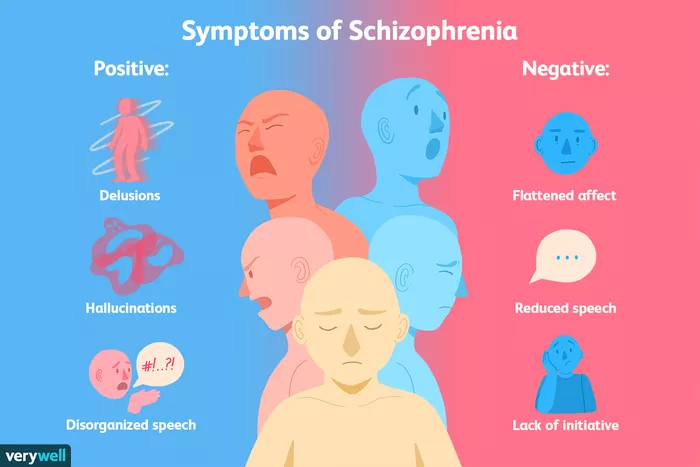
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Brain Abnormalities
Schizophrenia is purely a disease of the brain.
- If dopamine levels are high, there are too many receptors, and schizophrenia is intensified.
- Some display low brain activity in the frontal lobes and shrinkage of tissue.
- There is increased activity in the amygdala and thalamus.
- The fluid-filled spaces, known as the ventricles, in the interior of the brain's temporal lobes are often enlarged:
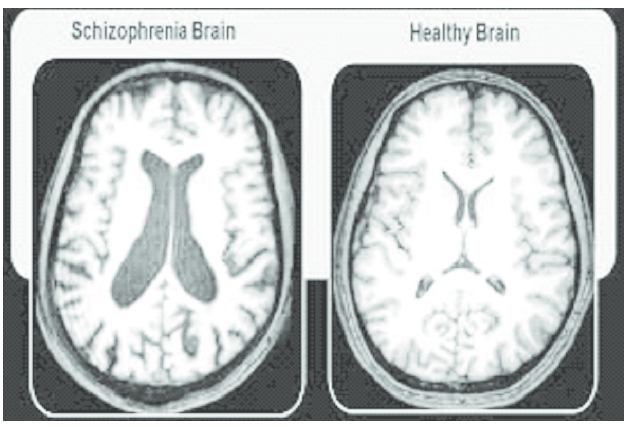
Image Courtesy of ResearchGate.
- Since it is very genetic, the risk could be increased during fetal development.- For example, if there is a pandemic, the mother is sick with the flu, or the mother lives in dense areas, there is an increased risk of schizophrenia.
- To explain acute schizophrenia, stress could turn on specific genes that eventually lead to the disorder. Remember, the environment influences gene expression and behavior!
- These are mainly biological factors, and there are no psychological factors unless an underlying biological factor is involved too.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.