<< Hide Menu
7.7 Behaviorism and Social Cognitive Theories of Personality
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Social-Cognitive Theories
Social Cognitive Theories emphasize the way personalities influence and are influenced by our interactions with our environment. They elaborate on how personalities are affected by principles of learning 📚, cognition, and social behavior 🗣️
- personal-construct theory: people develop their own system of constructs in order to better understand the world
- fundamental postulate: people's behavior is influenced by their thinking, so we can easily predict what they will do in the future by knowing what they did in the past
Reciprocal Determinism
Albert Bandura, who is also known for the social learning theory in unit 4, came up with this idea of reciprocal determinism. He found that children modeled the behaviors of the adults, even if it meant hitting a Bobo doll. You could see the influence of the Bobo doll experiment in his personality theory; it features imitation and modeling 🦆
Bandura believed that personality can change depending on one's thoughts, the environment, and behavior. It's a three way system.
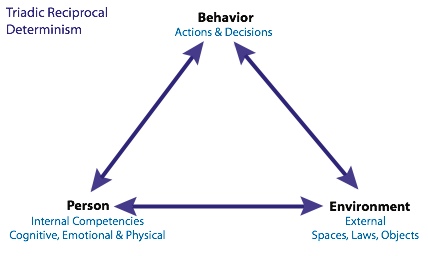
Image Courtesy of UK Essays.
Locus of Control
Do you control fate or does fate control you? There are two different loci of control:
An internal locus of control is where you believe you 👤 can control fate and what happens in your life. Having an internal locus of control is healthier because you actually take control of what happens to you and you can make choices 🧠
An external locus of control is where you believe the world determines what happens to you and there is no way you could change it. You have no choice but to live the way fate "wants" you to.
Learned Helplessness
Learned Helplessness is a state in which an organism has learned to resign itself to repeated aversive events as they believe that they have no control over their lives. They feel helpless, hopeless, and depressed. This goes hand in hand with an external locus of control.
It's one of the underlying causes of depression. An example is if a lifelong smoker 🚬 tries to quit repeatedly and fails every time. They just end up feeling hopeless and at some point, they might give up.
Optimism vs Pessimism
You could either lead your life with an optimistic 😊 outlook or pessimistic outlook 😔 Social-cognitive psychologists always emphasized our sense of personal control, which directly impacts how we lead our lives 🧗
- Those that have a sense of personal control usually lead life with an optimistic outlook because they know they could make changes in their lives. Those that don't have a sense of control usually think pessimistically and believe there is no way to change their lives. People with an optimistic personality always look on the positive side of things. Their personality seems to be uplifting and people love to be around them, while in contrast, a pessimistic personality always seems to look at the negative.
Each has its good points and its bad and success usually comes with a balance between the two. Someone should be optimistic enough to remain hopeful but pessimistic enough to know the extent to which they can succeed 🏆
An Individual
You, yourself, are an organizer of thoughts, desires, emotion, and personality.
Self-Esteem🥇
Your self-esteem is how much you value yourself. If someone has a high self-esteem, they feel confident and able to reach their goals. With a low self-esteem, it is hard to get anywhere, as some don't feel comfortable in their own skin.
Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy refers to your ability to have confidence in completing a task. Believe in yourself, you can do anything you set your mind to!
Individuals that have a high self-esteem and self-efficacy feel really good about themselves, sleep better, tend to be less anxious, are persistent, understand their self-worth, and put themselves up to challenges.
Self-Serving Bias
This is where most people are likely to perceive themselves favorably. An example of this would be accepting when good things happen and attributing it to their hard work and dedication, while rejecting when bad things happen and blaming it on others.
This occurs a lot in school, and maybe you've experienced it. If you've gotten a good grade on a test 💯, you probably were really proud of yourself and attributed it to your studying and hard work. However, if you got a bad grade, you'd blame the teacher and how hard the exam was.
Positive Psychology
There is a realm in psychology that deals with a positive well-being, positive health, and positive education. It is mainly studied by someone called Martin Seligman, and he aims to help individuals thrive.
Behavioral Theories
Behavioral theories focus more on the effect of learning 📚 on our personalities. This brings back unit 4 and conditioning; we are conditioned to repeat effective behaviors and continue to learn from the environment around us.
There isn't much about behavior and personality but you should understand that conditioning can influence our personality and the way we live our lives everyday.
Skinner argued that personality is determined by environment. According to this behaviorist thinking, we would be able to change one's personality simply by changing one's environment. This, however, has obvious shortcomings as it doesn't really take into account cognition.
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Personality Theories
🏆 Trivia— Personality, Motivation, and Emotion

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.